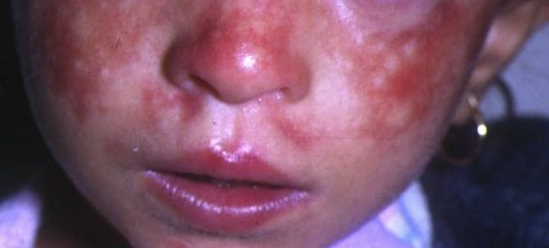
Bloom Syndrome: FDA permits marketing of first direct-to-consumer genetic carrier test
Last Updated on February 22, 2015 by Joseph Gut – thasso
 Along with this authorization, the FDA is also classifying carrier screening tests as class II. In addition, the FDA intends to exempt these devices from FDA premarket review. The agency plans to issue a notice that announces the intent to exempt these tests and that provides a 30-day period for public comment. This action creates the least burdensome regulatory path for autosomal recessive carrier screening tests with similar uses to enter the market.
Along with this authorization, the FDA is also classifying carrier screening tests as class II. In addition, the FDA intends to exempt these devices from FDA premarket review. The agency plans to issue a notice that announces the intent to exempt these tests and that provides a 30-day period for public comment. This action creates the least burdensome regulatory path for autosomal recessive carrier screening tests with similar uses to enter the market.
“The FDA believes that in many circumstances it is not necessary for consumers to go through a licensed practitioner to have direct access to their personal genetic information. Today’s authorization and accompanying classification, along with FDA’s intent to exempt these devices from FDA premarket review, supports innovation and will ultimately benefit consumers,” said Alberto Gutierrez, Ph.D., director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “These tests have the potential to provide people with information about possible mutations in their genes that could be passed on to their children.”
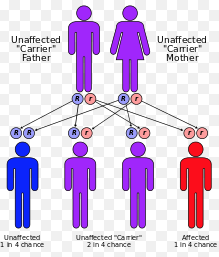
In general, carrier testing is a type of genetic testing performed on people who display no symptoms for a genetic disorder but may be at risk for passing it on to their children. A carrier for a genetic disorder has inherited one normal and one abnormal allele for a gene associated with the disorder. A child must inherit two abnormal alleles, one copy from each parent, in order for symptoms to appear.

